Features
Spectroelectrochemistry (SEC) is aimed at the investigation of electrochemical reaction mechanism and the interface structure between electrolyte solution and electrode. Remarkable progress in this field and related technology enables SEC to be applied in wide areas.
Nowadays, the relation between absorbance and potential for reversible or quasi-reversible system is theoretically elucidated, on which basis the analysis of electrochemical characteristics becomes possible for the system otherwise difficult with only the result of voltammogram.
Typical example is redox enzyme cytochrome c and methylene blue.
- Two varieties optical path length (0.5 and 1.0 mm)
- Designed to use the 6.0 mm reference electrode
- Two varieties of working electrodes (Au or Pt)
- Be able to use in a standard spectrometer
Overview
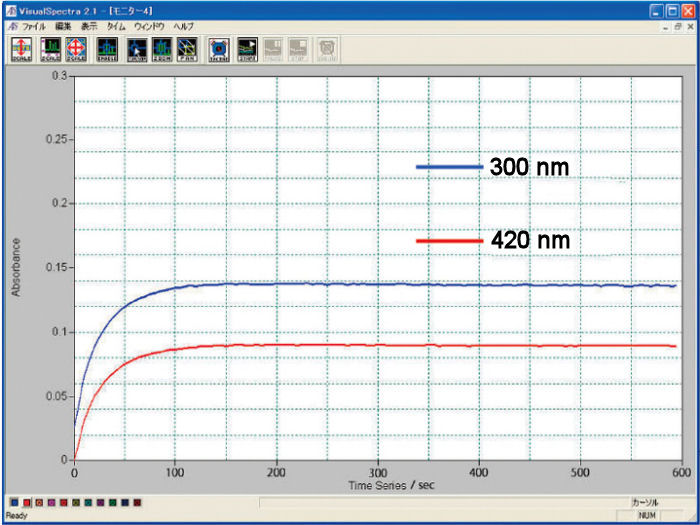
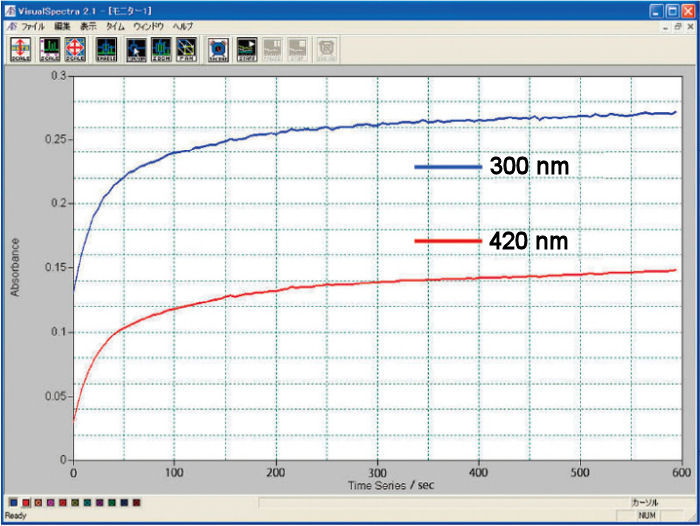
Comparison of 0.5 and 1.0 optical path length cell
The electrolysis stabilization time for the 0.5 mm optical path length cell is theoretically a half, compared with the 1.0 mm cell. It is the opposite, for the concentration, when the same result for the 1.0 mm cell is possible for a half of the concentration compared with the 0.5 mm cell. You could select the optical path length and the working electrode appropriate for your research purpose.
Optical path length
|
Merit
|
Demerit
|
| 0.5 mm |
High electrolytic speed |
Difficult maintenance |
| 1.0 mm |
Easy maintenance |
Slow electrolytic speed |
Comparison of the electrolysis reaction equilibrium time
For the comparison of the 0.5 and 1.0 optical path length cells, there is a difference between the theoretical and experimental values. It is in consequence of the experimental conditions.